BIM for Industrial Buildings
Leveraging the Latest Trends to Drive Efficiency, Collaboration, and Sustainability
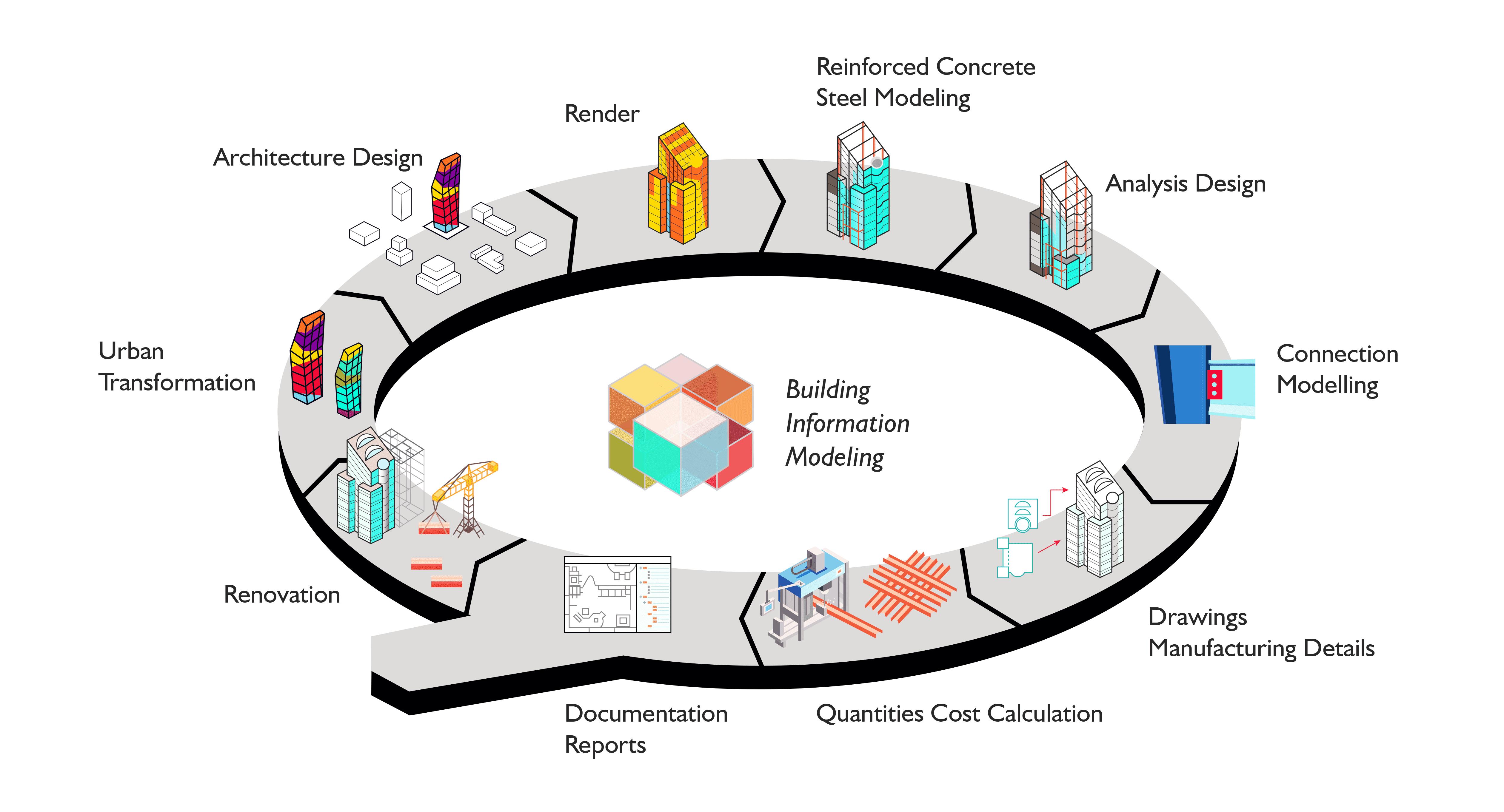
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has become a game-changer in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry, transforming how projects are planned, designed, executed, and maintained. With its collaborative, intelligent, and 3D model-based approach, BIM enhances efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability across all stages of construction projects. This is especially significant in industrial buildings, where complexity, scale, and performance are critical factors. In recent years, new trends have emerged within BIM for industrial buildings, underscoring the technology’s potential to revolutionize construction practices. This blog post delves into the latest trends in BIM for industrial buildings and explores how they can enhance efficiency, foster collaboration, and drive sustainability in construction projects.
1. The Rising Wave of BIM Mandates
Governments and regulatory bodies around the globe are increasingly mandating the use of BIM in construction projects, recognizing its potential to improve project outcomes and ensure consistency in construction standards. BIM mandates are aimed at standardizing practices across the AEC industry, promoting a culture of collaboration, transparency, and data-driven decision-making.
For industrial buildings, where precision and coordination are paramount, these mandates are a boon. They encourage stakeholders—from architects and engineers to contractors and facility managers—to adopt a unified approach to project planning and execution. By integrating BIM mandates, industrial construction projects benefit from reduced risks, minimized errors, and improved timelines. The standardized data formats and workflows facilitated by BIM also make it easier to meet compliance requirements, monitor progress, and ensure that project objectives align with regulatory standards. This standardization promotes a consistent, streamlined approach to project delivery, which is especially crucial in complex industrial projects involving multiple teams and intricate requirements.
2. The Power of Automation in BIM Processes
One of the most transformative trends in BIM for industrial buildings is the adoption of automation. Automation is reshaping traditional construction processes by enhancing productivity, accuracy, and efficiency. Key aspects of BIM automation include clash detection, quantity take-offs, model generation, and scheduling, all of which are integral to industrial construction projects.
For example, automated clash detection allows teams to identify and resolve conflicts between different building systems (e.g., HVAC, electrical, plumbing) before construction begins. This reduces costly rework and delays. Similarly, automated quantity take-offs and cost estimation help project managers forecast budgets more accurately and control project costs more effectively. By reducing manual interventions, automation allows teams to focus on more complex and creative tasks, such as optimizing building designs and improving construction methodologies. Ultimately, automation in BIM processes contributes to faster decision-making, reduced errors, and better project outcomes in industrial construction.
3. Digital Twins: A New Paradigm in Industrial Construction
The concept of Digital Twins is gaining significant traction in the realm of industrial construction. A Digital Twin is a virtual representation of a physical construction asset throughout its lifecycle, allowing project teams to simulate, analyze, and optimize performance. By creating a dynamic digital replica of an industrial facility, stakeholders can make more informed decisions, reduce uncertainties, and enhance overall project efficiency.
Digital Twins enable real-time monitoring and management of industrial buildings, offering insights into everything from energy consumption and equipment performance to maintenance needs and environmental conditions. This leads to improved asset management, extended lifespan of facilities, and reduced operational costs. Moreover, Digital Twins can be integrated with other technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) to predict and prevent equipment failures, optimize energy usage, and enhance safety protocols. In essence, Digital Twins serve as a powerful tool for industrial building stakeholders, providing a comprehensive, data-driven approach to managing building performance and sustainability.
4. Cloud-Based BIM: Enabling Seamless Collaboration
The shift to cloud-based BIM solutions is another key trend that is reshaping the AEC industry. Cloud technology has revolutionized how project teams collaborate, offering real-time data accessibility, seamless information exchange, and enhanced security. For industrial construction projects, where collaboration between multiple stakeholders is essential, cloud-based BIM solutions provide an unparalleled level of scalability and flexibility.
Cloud-based BIM platforms allow project teams to work collaboratively from different geographical locations, breaking down silos and fostering a more integrated project delivery approach. This real-time collaboration leads to faster decision-making, reduced errors, and better communication among stakeholders. Additionally, cloud-based BIM enables project data to be stored centrally, ensuring that all team members have access to the most up-to-date information, drawings, and models. This minimizes the risk of outdated or inaccurate data, which can lead to costly errors in industrial construction projects. The cloud-based approach also facilitates version control, enhances data security, and allows for easy scalability, accommodating the growing needs of complex industrial projects.
5. Prefabrication Integration with BIM: Streamlining Construction Timelines
The integration of BIM with prefabrication processes represents a natural progression in the construction industry. Prefabrication involves manufacturing building components off-site in a controlled environment and then assembling them on-site. When combined with BIM, prefabrication can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and accelerate construction timelines.
BIM facilitates accurate design and coordination, ensuring that prefabricated components fit perfectly when assembled on-site. This reduces the likelihood of errors and rework, leading to a more streamlined construction process. In industrial construction, where projects often involve repetitive elements and large-scale components, the integration of BIM with prefabrication can result in substantial time and cost savings. It also supports sustainable construction practices by minimizing material waste and reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation and on-site activities. By leveraging BIM for prefabrication, industrial construction firms can achieve higher quality standards, optimize resource utilization, and deliver projects more efficiently.
6. 4D and 5D BIM: Enhancing Project Planning and Management
BIM technology is evolving beyond traditional 3D modeling to incorporate 4D (time) and 5D (cost) simulations. These additional dimensions provide a more comprehensive view of a construction project, allowing teams to visualize the construction sequence and associated costs over time. This trend is particularly valuable in industrial construction, where project schedules and budgets are often complex and tightly controlled.
4D BIM integrates the time aspect with 3D models, enabling project teams to create detailed construction schedules and visualize the building process from start to finish. This allows stakeholders to identify potential scheduling conflicts, optimize workflows, and allocate resources more effectively. On the other hand, 5D BIM adds a cost dimension, allowing for real-time cost estimation and financial planning. This integration helps project managers track expenses, manage budgets, and make data-driven decisions to control costs throughout the project lifecycle. By adopting 4D and 5D BIM, industrial construction firms can improve project planning, enhance risk management, and achieve better project outcomes.
7. IoT Integration with BIM: Real-Time Data for Improved Performance
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of smart building design, and its integration with BIM is an emerging trend in industrial construction. IoT devices embedded within buildings can provide real-time data on various aspects of a building’s performance, such as energy usage, temperature, humidity, air quality, and equipment status. This data can be integrated into the BIM model, creating a dynamic and continuously updated digital representation of the building.
By combining IoT with BIM, project teams can monitor building performance in real time and make proactive decisions to optimize operations and maintenance. For instance, IoT sensors can detect anomalies in equipment performance and trigger preventive maintenance actions before a failure occurs, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of assets. Moreover, the integration of IoT and BIM supports sustainable building management by enabling continuous monitoring of energy consumption and environmental impact, helping to reduce energy costs and carbon emissions. For industrial buildings, where operational efficiency and safety are critical, the IoT-BIM integration provides a powerful tool to enhance building performance and sustainability.
8. BIM for Facility Management: Beyond Construction
While BIM is primarily associated with the design and construction phases of a project, its value extends well beyond these stages, particularly in the realm of facility management. For industrial buildings, where ongoing maintenance, repairs, and upgrades are essential, BIM serves as a comprehensive database that stores valuable information about the building’s systems, components, and history.
Facility managers can use BIM models to access real-time data on building elements, track maintenance schedules, and plan future upgrades. This enhances the efficiency of facility management operations and helps in making data-driven decisions that can prolong the lifespan of building assets and reduce maintenance costs. Furthermore, BIM for facility management enables better emergency preparedness by providing quick access to building information, such as fire exits, equipment locations, and utility connections. By leveraging BIM for facility management, industrial building owners and operators can achieve long-term value, optimize operational efficiency, and enhance occupant safety and comfort.
9. Sustainability and BIM: Designing Greener Industrial Buildings
Sustainability is a growing concern in the construction industry, and BIM plays a crucial role in designing greener industrial buildings. BIM enables project teams to analyze and optimize various aspects of a building’s environmental performance, from energy consumption and water usage to waste reduction and material selection.
Using BIM, architects and engineers can simulate different design scenarios and evaluate their environmental impact, helping them make informed decisions to reduce carbon footprints and enhance sustainability. For example, BIM can be used to optimize building orientation, natural lighting, and ventilation systems to minimize energy consumption. Additionally, BIM facilitates the selection of sustainable materials and construction methods, further promoting eco-friendly practices. In the context of industrial buildings, where energy consumption and environmental impact are significant concerns, BIM-driven sustainability strategies can result in substantial cost savings, regulatory compliance, and a positive brand image.
10. The Future of BIM in Industrial Construction
The future of BIM in industrial construction looks promising, with continuous advancements in technology and practices driving the industry forward. The integration of BIM with emerging technologies such as AI, machine learning, blockchain, and augmented reality (AR) is expected to further revolutionize industrial construction processes, enabling even greater efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration.